MPI_Group_range_incl
Creates a new group from ranges of ranks in an existing groupint MPI_Group_range_incl( MPI_Group group, int n, int ranges[][3], MPI_Group *newgroup );
Parameters
- group
- [in] group (handle)
- n
- [in] number of triplets in array ranges (integer)
- ranges
- [in] a one-dimensional array of integer triplets, of the form (first rank, last rank, stride) indicating ranks in group or processes to be included in newgroup.
- newgroup
- [out] new group derived from above, in the order defined by ranges (handle)
Remarks
If ranges consist of the triplets
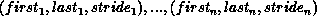
then newgroup consists of the sequence of processes in group with ranks
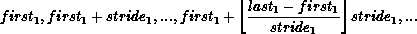

Each computed rank must be a valid rank in group and all computed ranks must be distinct, or else the program is erroneous. Note that we may have firsti > lasti, and stridei may be negative, but cannot be zero.
The functionality of this routine is specified to be equivalent to expanding the array of ranges to an array of the included ranks and passing the resulting array of ranks and other arguments to MPI_GROUP_INCL. A call to MPI_GROUP_INCL is equivalent to a call to MPI_GROUP_RANGE_INCL with each rank i in ranks replaced by the triplet (i,i,1) in the argument ranges.
Thread and Interrupt Safety
This routine is thread-safe. This means that this routine may be safely used by multiple threads without the need for any user-provided thread locks. However, the routine is not interrupt safe. Typically, this is due to the use of memory allocation routines such as malloc or other non-MPICH runtime routines that are themselves not interrupt-safe.
Notes for Fortran
All MPI routines in Fortran (except for MPI_WTIME and MPI_WTICK) have an additional argument ierr at the end of the argument list. ierr is an integer and has the same meaning as the return value of the routine in C. In Fortran, MPI routines are subroutines, and are invoked with the call statement.All MPI objects (e.g., MPI_Datatype, MPI_Comm) are of type INTEGER in Fortran.
Errors
All MPI routines (except MPI_Wtime and MPI_Wtick) return an error value; C routines as the value of the function and Fortran routines in the last argument. Before the value is returned, the current MPI error handler is called. By default, this error handler aborts the MPI job. The error handler may be changed with MPI_Comm_set_errhandler (for communicators), MPI_File_set_errhandler (for files), and MPI_Win_set_errhandler (for RMA windows). The MPI-1 routine MPI_Errhandler_set may be used but its use is deprecated. The predefined error handler MPI_ERRORS_RETURN may be used to cause error values to be returned. Note that MPI does not guarentee that an MPI program can continue past an error; however, MPI implementations will attempt to continue whenever possible.
- MPI_SUCCESS
- No error; MPI routine completed successfully.
- MPI_ERR_GROUP
- Null or invalid group passed to function.
- MPI_ERR_INTERN
- This error is returned when some part of the MPICH implementation is unable to acquire memory.
- MPI_ERR_ARG
- Invalid argument. Some argument is invalid and is not identified by a specific error class (e.g., MPI_ERR_RANK).
- MPI_ERR_RANK
- Invalid source or destination rank. Ranks must be between zero and the size of the communicator minus one; ranks in a receive (MPI_Recv, MPI_Irecv, MPI_Sendrecv, etc.) may also be MPI_ANY_SOURCE.
See Also
MPI_Group_freeExample Code
The following sample code illustrates MPI_Group_range_incl.
#include "mpi.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main( int
argc, char *argv[] )
{
MPI_Group g1, g2, g4, g5, g45, selfgroup, g6;
int ranks[16],
size, rank, myrank, range[1][3];
int errs = 0;
int i, rin[16],
rout[16], result;
MPI_Init(0,0);
MPI_Comm_group( MPI_COMM_WORLD, &g1 );
MPI_Comm_rank( MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myrank );
MPI_Comm_size( MPI_COMM_WORLD, &size );
if (size < 8) {
fprintf( stderr, "Test requires 8 processes (16 prefered) only %d
provided\n", size ); fflush(stdout);
MPI_Abort(MPI_COMM_WORLD, 1);
}
/* 16 members, this process is rank 0,
return in group 1 */
ranks[0] = myrank; ranks[1] = 2; ranks[2] = 7;
if (myrank == 2)
ranks[1] = 3;
if (myrank == 7)
ranks[2] = 6;
MPI_Group_incl( g1, 3, ranks, &g2 );
/* Check the resulting group */
MPI_Group_size( g2, &size );
MPI_Group_rank( g2, &rank );
if (size != 3) {
fprintf( stderr, "Size should be %d, is %d\n", 3, size );fflush(stderr);
errs++;
}
if (rank != 0) {
fprintf( stderr, "Rank should be %d, is %d\n", 0, rank );fflush(stderr);
errs++;
}
rin[0] = 0; rin[1] = 1; rin[2] = 2;
MPI_Group_translate_ranks( g2, 3, rin, g1, rout );
for (i=0; i<3;
i++) {
if (rout[i] !=
ranks[i]) {
fprintf( stderr, "translated rank[%d] %d should be %d\n", i, rout[i], ranks[i]
);fflush(stderr);
errs++;
}
}
/* Translate the process of the self
group against another group */
MPI_Comm_group( MPI_COMM_SELF, &selfgroup );
rin[0] = 0;
MPI_Group_translate_ranks( selfgroup, 1, rin, g1, rout );
if (rout[0] !=
myrank) {
fprintf( stderr, "translated of self is %d should be %d\n", rout[0], myrank
);fflush(stderr);
errs++;
}
for (i=0; i<size;
i++)
rin[i] = i;
MPI_Group_translate_ranks( g1, size, rin, selfgroup, rout );
for (i=0; i<size;
i++) {
if (i == myrank
&& rout[i] != 0) {
fprintf( stderr, "translated world to self of %d is %d\n", i, rout[i]
);fflush(stderr);
errs++;
}
else
if (i != myrank && rout[i]
!= MPI_UNDEFINED) {
fprintf( stderr, "translated world to self of %d should be undefined, is
%d\n", i, rout[i] );
errs++;
}
}
MPI_Group_free( &selfgroup );
/* Exclude everyone in our group */
{
int i, *ranks,
g1size;
MPI_Group_size( g1, &g1size );
ranks = (int *)malloc(
g1size * sizeof(int)
);
for (i=0; i<g1size;
i++) ranks[i] = i;
MPI_Group_excl( g1, g1size, ranks, &g6 );
if (g6 !=
MPI_GROUP_EMPTY) {
fprintf( stderr, "Group formed by excluding all ranks not empty\n"
);fflush(stderr);
errs++;
MPI_Group_free( &g6 );
}
free( ranks );
}
MPI_Group_free( &g2 );
range[0][0] = 1;
range[0][1] = size-1;
range[0][2] = 2;
MPI_Group_range_excl( g1, 1, range, &g5 );
range[0][0] = 1;
range[0][1] = size-1;
range[0][2] = 2;
MPI_Group_range_incl( g1, 1, range, &g4 );
MPI_Group_union( g4, g5, &g45 );
MPI_Group_compare( MPI_GROUP_EMPTY, g4, &result );
if (result !=
MPI_UNEQUAL) {
errs++;
fprintf( stderr, "Comparison with empty group gave %d, not 3\n", result );fflush(stderr);
}
MPI_Group_free( &g4 );
MPI_Group_free( &g5 );
MPI_Group_free( &g45 );
/* Now, duplicate the test, but using
negative strides */
range[0][0] = size-1;
range[0][1] = 1;
range[0][2] = -2;
MPI_Group_range_excl( g1, 1, range, &g5 );
range[0][0] = size-1;
range[0][1] = 1;
range[0][2] = -2;
MPI_Group_range_incl( g1, 1, range, &g4 );
MPI_Group_union( g4, g5, &g45 );
MPI_Group_compare( MPI_GROUP_EMPTY, g4, &result );
if (result !=
MPI_UNEQUAL) {
errs++;
fprintf( stderr, "Comparison with empty group (formed with negative strides)
gave %d, not 3\n", result );fflush(stderr);
}
MPI_Group_free( &g4 );
MPI_Group_free( &g5 );
MPI_Group_free( &g45 );
MPI_Group_free( &g1 );
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
DOWNLOAD
Win32 DeinoMPI.2.0.1.msi
Win64 DeinoMPI.x64.2.0.1.msi